Albert Einstein is often quoted as saying that compound interest is “the most powerful force in the universe.” The quote is probably apocryphal, but it reflects a mathematical truth. Interest on earlier interest grows exponentially, outrunning the linear growth of revenue and eventually consuming everything.
That is where the United States now stands. The government does pay the interest on its debt every year, but it is having to pay it with borrowed money. The interest curve is rising exponentially, while the tax base is not.
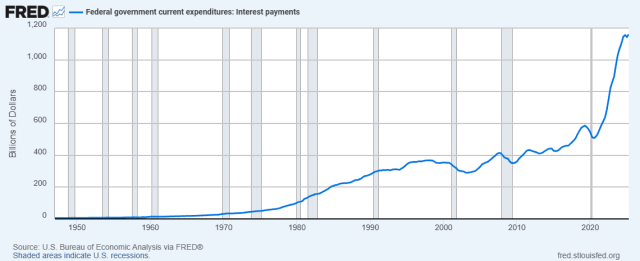
Interest is now the fastest growing line item in the entire federal budget. The government paid $970 billion in net interest in FY2025, more than the Pentagon budget and rapidly closing in on Social Security. It already exceeds spending on Medicare and national defense and is second only to Social Security. The Congressional Budget Office projects that interest will reach nearly $1.8 trillion by 2035 and will cost taxpayers $13.8 trillion over the next decade. That is roughly what Social Security will pay out over the same decade (about $1.6 trillion a year). The Social Security Trust Fund is running dry, not because there are too many seniors, but because interest payments are consuming the federal budget that should be shoring it up.
Continue readingFiled under: Ellen Brown Articles/Commentary | Tagged: compound interest, economics, economy, Federal Reserve, FINANCE, Inflation, money, national debt, seigniorage, Trillion dollar coin | 7 Comments »








Regime Change at the Fed: From Big Bank Bailouts to Local Productivity
Image by ScheerPost.
On January 30, when former Federal Reserve board member Kevin Warsh was nominated by President Trump as the central bank’s next chair, markets sold off and gold and silver plunged. Investors were positioned for a “dove,” someone inclined to cut rates aggressively and keep money loose; and Warsh has a long-standing reputation as a “hawk.”
So wrote Michael Nicoletos in an article titled “Everyone Is Focusing on the Wrong Thing.” But Nicoletos and some other commentators are seeing something else on the horizon – a rebalancing of the banking system through an overhaul of the Federal Reserve itself. In recent months, noted Nicoletos, Warsh has argued that the central bank’s “bloated balance sheet” has made borrowing “too easy” for Wall Street, while leaving “credit on Main Street too tight.” That contrast — abundant liquidity for the largest financial institutions, scarcity for the communities that actually generate economic activity — is a structural flaw that has unbalanced the American economy.
Continue reading →Filed under: Ellen Brown Articles/Commentary | Tagged: Bank of North Dakota, community banks, economics, economy, Federal Reserve, FINANCE, Financial Regulation, Kevin Warsh, money, NATIONAL INFRASTRUCTURE BANK, politics, Public Banking, quantitative easing, Scott Bessent | 3 Comments »